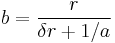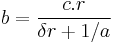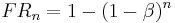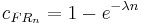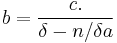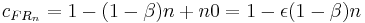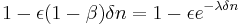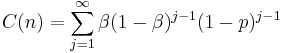Mathematical principles of reinforcement
Mathematical principles of reinforcement (MPR) are a set of mathematical equations that attempt to describe and predict the most fundamental aspects of behavior. The three key principles of MPR, arousal, constraint, and coupling, describe how incentives motivate responding, how time constrains it, and how reinforcers become associated with specific responses, respectively. Mathematical models are provided for these basic principles in order to articulate the necessary detail of actual data (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003).
The first basic principle of MPR is arousal. Arousal refers to the activation of behavior by the presentation of incentives. An increase in activity level following repeated presentations of incentives is a fundamental aspect of conditioning. Killeen, Hanson, and Osborne (1978) proposed that adjunctive (or schedule induced) behaviors are normally occurring parts of an organism’s repertoire. Delivery of incentives increases the rate of adjunctive behaviors by generating a heightened level of general activity, or arousal, in organisms.
Killeen & Hanson (1978) exposed pigeons to a single daily presentation of food in the experimental chamber and measured general activity for 15 minutes after a feeding. They showed that activity level increased slightly directly following a feeding and then decreased slowly over time. The rate of decay can be described by the following function:
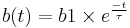
- b1 = y-intercept (responses per minute)
- t = time in seconds since feeding
 = time constant
= time constant- e = base of natural logarithm
The time course of the entire theoretical model of general activity is modeled by the following equation:
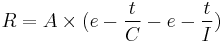
- A = arousal
- I = temporal inhibition
- C = competing behaviors
To better conceptualize this model, imagine how rate of responding would appear with each of these processes individually. In the absence of temporal inhibition or competing responses, arousal level would remain high and response rate would be depicted as an almost horizontal line with a very small negative slope. Directly following food presentation, temporal inhibition is at its maximum level. It decreases quickly as time elapses, and response rate would be expected to increase up to the level of arousal in a short time. Competing behaviors such as goal tracking or hopper inspection are at a minimum directly after food presentation. These behaviors increase as the interval elapses, so the measure of general activity would slowly decrease. Subtracting these two curves results in the predicted level of general activity.
Killeen et al. (1978) then increased the frequency of feeding from daily to every fixed-time seconds. They showed that general activity level increased substantially from the level of daily presentation. Response rate asymptotes were highest for the highest rates of reinforcement. These experiments indicate that arousal level is proportional to rate of incitement, and the asymptotic level increases with repeated presentations of incentives. The increase in activity level with repeated presentation of incentives is called cumulation of arousal. The first principle of MPR states that arousal level is proportional to rate of reinforcement, A=ar, where A= arousal level, a= specific activation, r= rate of reinforcement (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003).
An obvious but often overlooked factor when analyzing response distributions is that responses are not instantaneous, but take some amount of time to emit (Killeen, 1994). These ceilings on response rate are often accounted for by competition from other responses, but less often for the fact that responses cannot always be emitted at the same rate at which they are elicited (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003). This limiting factor must be taken into account in order to correctly characterize what responding could be theoretically, and what it will be empirically.
An organism may receive impulses to respond at a certain rate. At low rates of reinforcement, the elicited rate and emitted rate will approximate each other. At high rates of reinforcement, however, this elicited rate is subdued by the amount of time it takes to emit a response. Response rate, 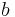 , is typically measured as the number of responses occurring in an epoch divided by the duration of an epoch. The reciprocal of
, is typically measured as the number of responses occurring in an epoch divided by the duration of an epoch. The reciprocal of 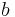 gives the typical measure of the inter response (IRT), the average time from the start of one response to the start of another (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003). This is actually the cycle time rather than the time between responses. According to Killeen & Sitomer (2003), the IRT consists of two subintervals, the time required to emit a response,
gives the typical measure of the inter response (IRT), the average time from the start of one response to the start of another (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003). This is actually the cycle time rather than the time between responses. According to Killeen & Sitomer (2003), the IRT consists of two subintervals, the time required to emit a response, 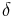 plus the time between responses,
plus the time between responses,  . Therefore, response rate can be measured either by dividing the number of responses by the cycle time:
. Therefore, response rate can be measured either by dividing the number of responses by the cycle time:
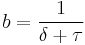 ,
,
or as the number of responses divided by the actual time between responses:
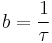 .
.
This instantaneous rate, 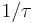 may be the best measure to use, as the nature of the operandum may change arbitrarily within an experiment (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003).
may be the best measure to use, as the nature of the operandum may change arbitrarily within an experiment (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003).
Killeen, Hall, Reilly, and Kettle (2002) showed that if instantaneous rate of responding is proportional to rate of reinforcement, 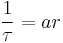 , then a fundamental equation for MPR results. Killeen & Sitomer (2003) showed that if
, then a fundamental equation for MPR results. Killeen & Sitomer (2003) showed that if 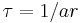 , then
, then 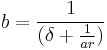 , and rearranging gives:
, and rearranging gives:
While responses may be elicited at a rate proportional to 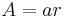 , they can only be emitted at rate
, they can only be emitted at rate 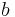 due to constraint. The second principle of MPR states that the time required to emit a response constrains response rate (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003).
due to constraint. The second principle of MPR states that the time required to emit a response constrains response rate (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003).
Coupling is the final concept of MPR that ties all of the processes together and allows for specific predictions of behavior with different schedules of reinforcement. Coupling refers to the association between responses and reinforcers. The target response is the response of interest to the experimenter, but any response can become associated with a reinforcer. Contingencies of reinforcement refer to how a reinforcer is scheduled with respect to the target response (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003), and the specific schedules of reinforcement in effect determine how responses are coupled to the reinforcer. The third principle of MPR states that the degree of coupling between a response and reinforcer decreases with the distance between them (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003). Coupling coefficients, designated as c, are given for the different schedules of reinforcement. When the coupling coefficients are inserted into the activation-constraint model, complete models of conditioning are derived:
This is the fundamental equation of MPR. The dot after 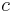 is a placeholder for the specific contingencies of reinforcement under study (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003).
is a placeholder for the specific contingencies of reinforcement under study (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003).
The rate of reinforcement for fixed-ratio schedules is easy to calculate, as reinforcement rate is directly proportional to response rate and inversely proportional to ratio requirement (Killeen, 1994). The schedule feedback function is therefore:
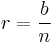 .
.
Substituting this function into the complete model gives the equation of motion for ratio schedules (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003). Killeen (2003) showed that the most recent response in a sequence of responses is weighted most heavily and given a weight of 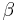 , leaving
, leaving 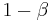 for the remaining responses. The penultimate response receives
for the remaining responses. The penultimate response receives 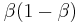 , the third back receives
, the third back receives 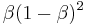 . The
. The  th response back is given a weight of
th response back is given a weight of 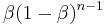 The sum of this series is the coupling coefficient for fixed-ratio schedules:
The sum of this series is the coupling coefficient for fixed-ratio schedules:
The continuous approximation of this is:
where is the intrinsic rate of memory decay. Inserting the reinforcement rate and coupling coefficient into the activation-constraint model gives the predicted response rates for FR schedules:
This equation predicts low response rates at low ratio requirements due to the displacement of memory by consummatory behavior. However, these low rates are not always found. Coupling of responses may extend back beyond the preceding reinforcer, and an extra parameter, 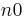 is added to account for this. Killeen & Sitomer (2003) showed that the coupling coefficient for FR schedules then becomes:
is added to account for this. Killeen & Sitomer (2003) showed that the coupling coefficient for FR schedules then becomes:
n0 is the number of responses preceding the prior reinforcer that contribute to response strength. 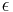 which ranges from 0 to 1 is then the degree of erasure of the target response from memory with the delivery of a reinforcer. (
which ranges from 0 to 1 is then the degree of erasure of the target response from memory with the delivery of a reinforcer. (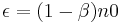 ) If
) If 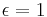 , erasure is complete and the simpler FR equation can be used.
, erasure is complete and the simpler FR equation can be used.
According to Killeen & Sitomer (2003), the duration of a response can affect the rate of memory decay. When response durations vary, either within or between organisms, then a more complete model is needed, and 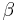 is replaced with
is replaced with 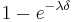 yielding:
yielding:
Idealized variable-ratio schedules with a mean response requirement of  have a constant probability of
have a constant probability of 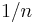 of a response ending in reinforcement (Bizo, Kettle, & Killeen, 2001). The last response ending in reinforcement must always occur and receives strengthening of
of a response ending in reinforcement (Bizo, Kettle, & Killeen, 2001). The last response ending in reinforcement must always occur and receives strengthening of 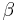 . The penultimate response occurs with probability
. The penultimate response occurs with probability 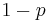 and receives a strengthening of
and receives a strengthening of 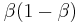 . The sum of this process up to infinity is (Killeen 2001, Appendix):
. The sum of this process up to infinity is (Killeen 2001, Appendix):
The coupling coefficient for VR schedules ends up being:
cVRn= n
n+(1-b)/b Multiplying by degree of erasure of memory gives:
cVRn= n
n+e(1-b)/b
The coupling coefficient can then be inserted into the activation-constraint model just as the coupling coefficient for FR schedules to yield predicted response rates under VR schedules:
b= cVRn/d-n/da In interval schedules, the schedule feedback function is R=1/t where t is the minimum average time between reinforcers (Killeen, 1994). Coupling in interval schedules is weaker than ratio schedules, as interval schedules equally strengthen all responses preceding the target rather than just the target response. Only some proportion r of memory is strengthened. With a response requirement, the final, target response must receive strength of b. All preceding responses, target or non-target, receive a strengthening of 1-b.
Fixed-time schedules are the simplest time dependent schedules in which organisms must simply wait t seconds for an incentive. Killeen (1994) reinterpreted temporal requirements as response requirements and integrated the contents of memory from one incentive to the next. This gives the contents of memory to be:
N MN= lò e-lndn 0 This is the degree of saturation in memory of all responses, both target and non-target, elicited in the context (Killeen, 1994). Solving this equation gives the coupling coefficient for fixed-time schedules: c=r(1-e-lbt) where r is the proportion of target responses in the response trajectory. Expanding into a power series gives the following approximation:
c» rlbt
1+lbt
This equation predicts serious instability for non-contingent schedules of reinforcement.
Fixed-interval schedules are guaranteed a strengthening of a target response, b=w1, as reinforcement is contingent on this final, contiguous response (Killeen, 1994). This coupling is equivalent to the coupling on FR 1 schedules w1=b=1-e-l. The remainder of coupling is due to the memory of preceding behavior. The coupling coefficient for FI schedules is: c= b +r(1- b -e-lbt). Variable-time schedules are similar to random ratio schedules in that there is a constant probability of reinforcement, but these reinforcers are set up in time rather than responses. The probability of no reinforcement occurring before some time t’ is an exponential function of that time with the time constant t being the average IRI of the schedule (Killeen, 1994). To derive the coupling coefficient, the probability of the schedule not having ended, weighted by the contents of memory, must be integrated.
∞
M= lò e-n’t/te-ln’ dn’
0
In this equation, t’=n’t, where t is a small unit of time. Killeen (1994) explains that the first exponential term is the reinforcement distribution, whereas the second term is the weighting of this distribution in memory. Solving this integral and multiplying by the coupling constant r, gives the extent to which memory is filled on VT schedules: c=rlbt
1+lbt
This is the same coupling coefficient as an FT schedule, except it is an exact solution for VT schedules rather than an approximation. Once again, the feedback function on these non-contingent schedules predicts serious instability in responding.
As with FI schedules, variable-interval schedules are guaranteed a target response coupling of b. Simply adding b to the VT equation gives:
∞
M= b+ lò e-n’t/te-ln’ dn’
1
Solving the integral and multiplying by r gives the coupling coefficient for VI schedules:
c= b+(1-b) rlbt
1+lbt
The coupling coefficients for all of the schedules are inserted into the activation-constraint model to yield the predicted, overall response rate. The third principle of MPR states that the coupling between a response and a reinforcer decreases with increased time between them (Killeen & Sitomer, 2003).
Mathematical principles of reinforcement describe how incentives fuel behavior, how time constrains it, and how contingencies direct it. It is a general theory of reinforcement that combines both contiguity and correlation as explanatory processes of behavior. Many responses preceding reinforcement may become correlated with the reinforcer, but the final response receives the greatest weight in memory. Specific models are provided for the three basic principles to articulate predicted response patterns in many different situations and under different schedules of reinforcement. Coupling coefficients for each reinforcement schedule are derived and inserted into the fundamental equation to yield overall predicted response rates.
References
- Bizo, L. A., Kettle, L. C. & Killeen, P. R. (2001). "Animals don't always respond faster for more food: The paradoxical incentive effect." Animal Learning & Behavior, 29, 66-78.
- Killeen, P.R. (1994). "Mathematical principles of reinforcement." Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 17, 105-172.
- Killeen, P. R., Hall, S. S., Reilly, M. P., & Kettle, L. C. (2002). "Molecular analyses of the principal components of response strength." Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 78, 127-160.
- Killeen, P. R., Hanson, S. J., & Osborne, S. R. (1978). "Arousal: Its genesis and manifestation as response rate." Psychological review. Vol 85 No 6. p. 571-81
- Killeen, P. R. & Sitomer, M. T. (2003). "MPR." Behavioural Processes, 62, 49-64